How To Use Animator In Marquee Avid
- After Effects User Guide
- Beta releases
- Beta Program Overview
- After Furnishings Beta Home
- Features in Beta
- Properties panel (Beta)
- Getting started
- Become started with After Effects
- What's new in After Effects
- Release Notes | Later on Effects
- Later Furnishings organization requirements
- Keyboard shortcuts in Subsequently Furnishings
- Supported File formats | Afterwards Effects
- Hardware recommendations
- After Furnishings for Apple tree silicon
- Planning and setup
- Setup and installation
- Workspaces
- General user interface items
- Go to know After Effects interface
- Workflows
- Workspaces, panels, and viewers
- Projects and compositions
- Projects
- Composition nuts
- Precomposing, nesting, and pre-rendering
- View detailed performance information with the Composition Profiler
- Picture palace 4D Composition Renderer
- Importing footage
- Preparing and importing still images
- Importing from After Effects and Adobe Premiere Pro
- Importing and interpreting video and sound
- Preparing and importing 3D image files
- Importing and interpreting footage items
- Working with footage items
- Detect edit points using Scene Edit Detection
- XMP metadata
- Text and Graphics
- Text
- Formatting characters and the Character panel
- Text effects
- Creating and editing text layers
- Formatting paragraphs and the Paragraph panel
- Extruding text and shape layers
- Animative text
- Examples and resources for text animation
- Live Text Templates
- Motion Graphics
- Piece of work with Motion Graphics templates in After Effects
- Apply expressions to create drop-down lists in Motion Graphics templates
- Work with Essential Backdrop to create Motion Graphics templates
- Supplant images and videos in Motion Graphics templates and Essential Properties
- Text
- Drawing, Painting, and Paths
- Overview of shape layers, paths, and vector graphics
- Paint tools: Brush, Clone Stamp, and Eraser
- How to taper shape strokes
- Shape attributes, paint operations, and path operations for shape layers
- Use Offset Paths shape effect to modify shapes
- Creating shapes
- Create masks
- Remove objects from your videos with the Content-Aware Fill panel
- Roto Brush and Refine Matte
- Layers, Markers, and Photographic camera
- Selecting and arranging layers
- Blending modes and layer styles
- 3D layers
- Layer properties
- Creating layers
- Managing layers
- Layer markers and limerick markers
- Cameras, lights, and points of involvement
- Animation, Keyframes, Move Tracking, and Keying
- Blitheness
- Animation basics
- Animative with Puppet tools
- Managing and animative shape paths and masks
- Animating Sketch and Capture shapes using After Effects
- Contrasted animation tools
- Work with Data-driven animation
- Keyframe
- Keyframe interpolation
- Setting, selecting, and deleting keyframes
- Editing, moving, and copying keyframes
- Motion tracking
- Tracking and stabilizing motion
- Face Tracking
- Mask Tracking
- Mask Reference
- Speed
- Time-stretching and time-remapping
- Timecode and time display units
- Keying
- Keying
- Keying effects
- Blitheness
- Transparency and Compositing
- Compositing and transparency overview and resources
- Alpha channels, masks, and mattes
- Adjusting color
- Color nuts
- Utilize the Adobe Color Themes extension
- Color management
- Color Correction effects
- Effects and Animation Presets
- Effects and animation presets overview
- Effect list
- Simulation furnishings
- Stylize effects
- Audio effects
- Distort furnishings
- Perspective effects
- Channel effects
- Generate effects
- Transition effects
- The Rolling Shutter Repair effect
- Blur and Sharpen effects
- 3D Aqueduct furnishings
- Utility effects
- Matte furnishings
- Noise and Grain furnishings
- Detail-preserving Upscale effect
- Obsolete furnishings
- Expressions and Automation
- Expression
- Expression basics
- Understanding the expression language
- Using expression controls
- Syntax differences betwixt the JavaScript and Legacy ExtendScript expression engines
- Editing expressions
- Expression errors
- Using the Expressions editor
- Use expressions to edit and access text properties
- Expression language reference
- Expression examples
- Automation
- Automation
- Scripts
- Expression
- Immersive video, VR, and 3D
- Construct VR environments in After Furnishings
- Apply immersive video effects
- Compositing tools for VR/360 videos
- Tracking 3D camera movement
- Work in 3D Pattern Space
- 3D Transform Gizmos
- Do more than with 3D animation
- Preview changes to 3D designs real time with the Real-Time Engine
- Add together responsive design to your graphics
- Views and Previews
- Previewing
- Video preview with Mercury Transmit
- Modifying and using views
- Rendering and Exporting
- Basics of rendering and exporting
- Export an After Furnishings project as an Adobe Premiere Pro project
- Converting movies
- Multi-frame rendering
- Automated rendering and network rendering
- Rendering and exporting still images and yet-prototype sequences
- Using the GoPro CineForm codec in After Effects
- Working with other applications
- Dynamic Link and After Effects
- Working with After Effects and other applications
- Sync Settings in After Effects
- Creative Cloud Libraries in After Effects
- Plug-ins
- Picture palace 4D and Cineware
- Collaboration: Frame.io, and Team Projects
- Collaboration in Premiere Pro and After Furnishings
- Frame.io
- Install and activate Frame.io
- Employ Frame.io with Premiere Pro and After Effects
- Frequently asked questions
- Squad Projects
- Get Started with Team Projects
- Create a Squad Project
- Collaborate with Team Projects
- Memory, storage, performance
- Memory and storage
- Amend performance
- Preferences
- GPU and GPU driver requirements for After Effects
Use the Legacy or Advanced Puppet tools to quickly add natural motility to raster images and vector graphics, including even so images, shapes, and text characters.
Though the Puppet tools work within an effect (the Puppet consequence), you don't apply the effect using the Upshot carte or the Effects & Presets panel. Use the Puppet tools in the Tools panel to direct apply and work with the effect in the Layer console or Composition panel.
The Boob effect works by deforming part of an prototype co-ordinate to the positions of pins that you place and movement. These pins define what parts of the prototype moves, what parts remain rigid, and what parts are be in front end when parts overlap.
Each Boob tool is used to identify and modify a specific type of pin:
Puppet Pin tool
![]()
Utilize this tool to place and move Deform pins.
Puppet Overlap tool
![]()
Use this tool to place Overlap pins, which indicate which parts of an image should announced in front of others when distortion causes parts of the paradigm to overlap one some other.
Puppet Starch tool
![]()
Employ this tool to place Starch pins, which stiffen parts of the image so that they are distorted less.

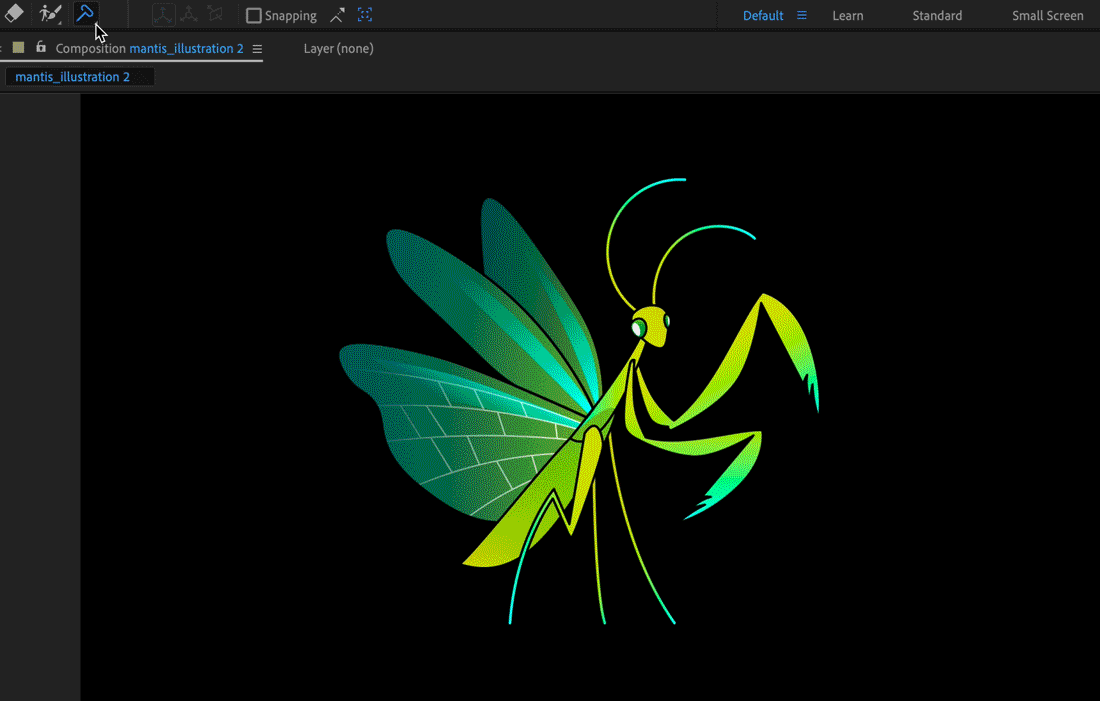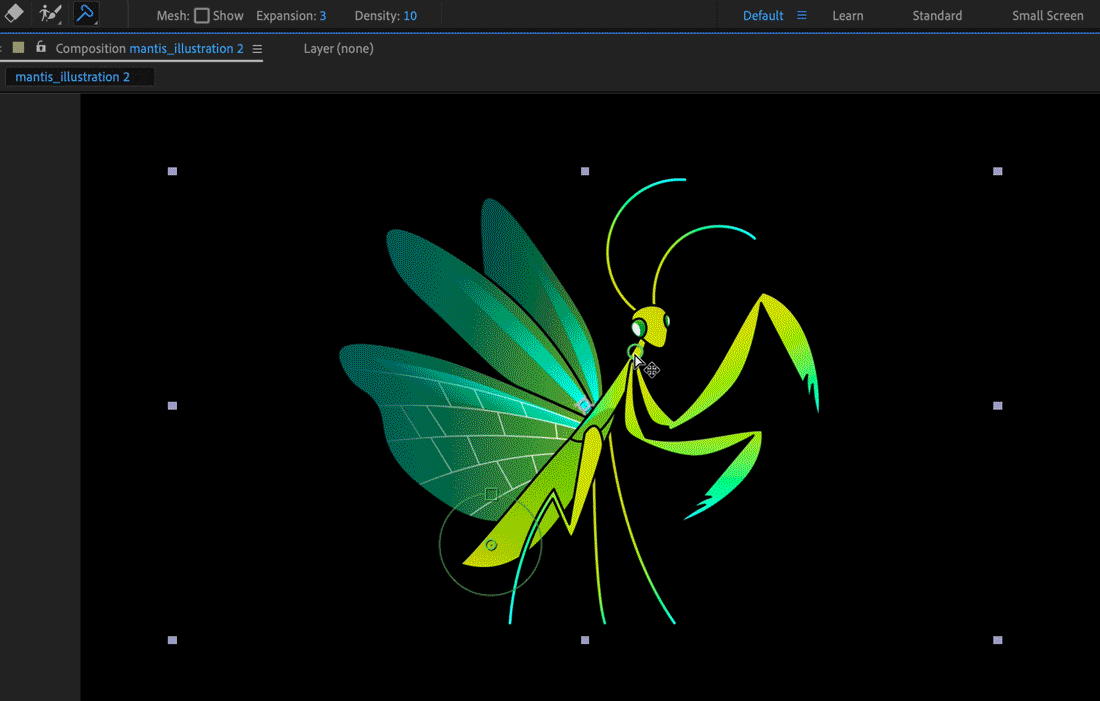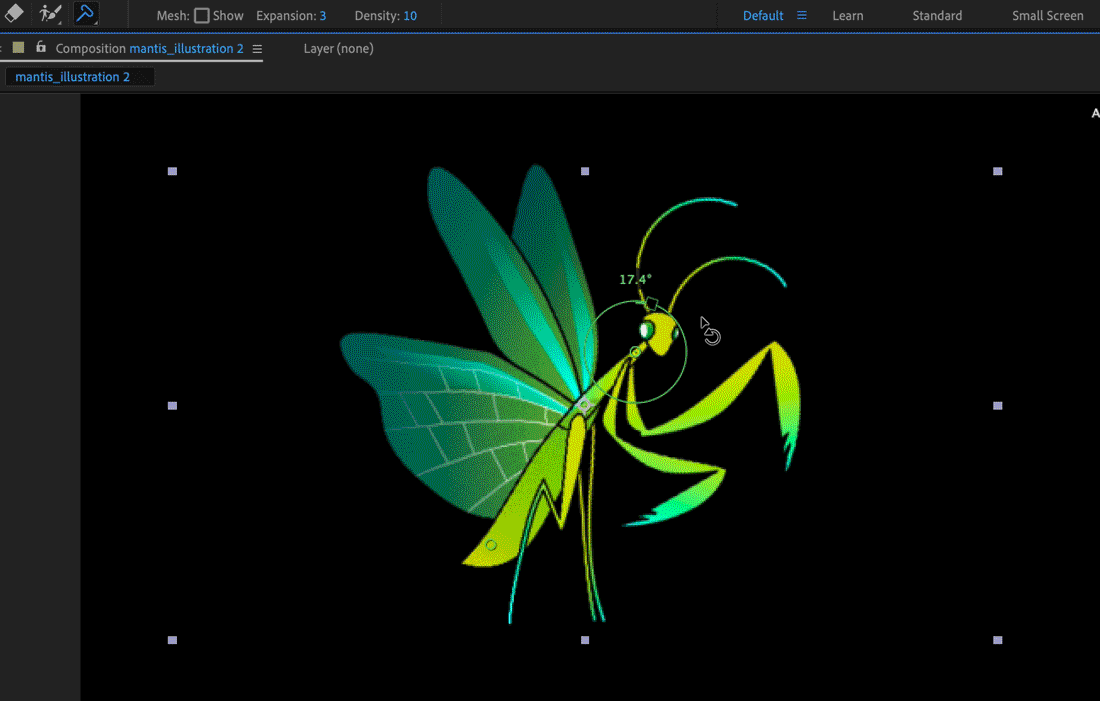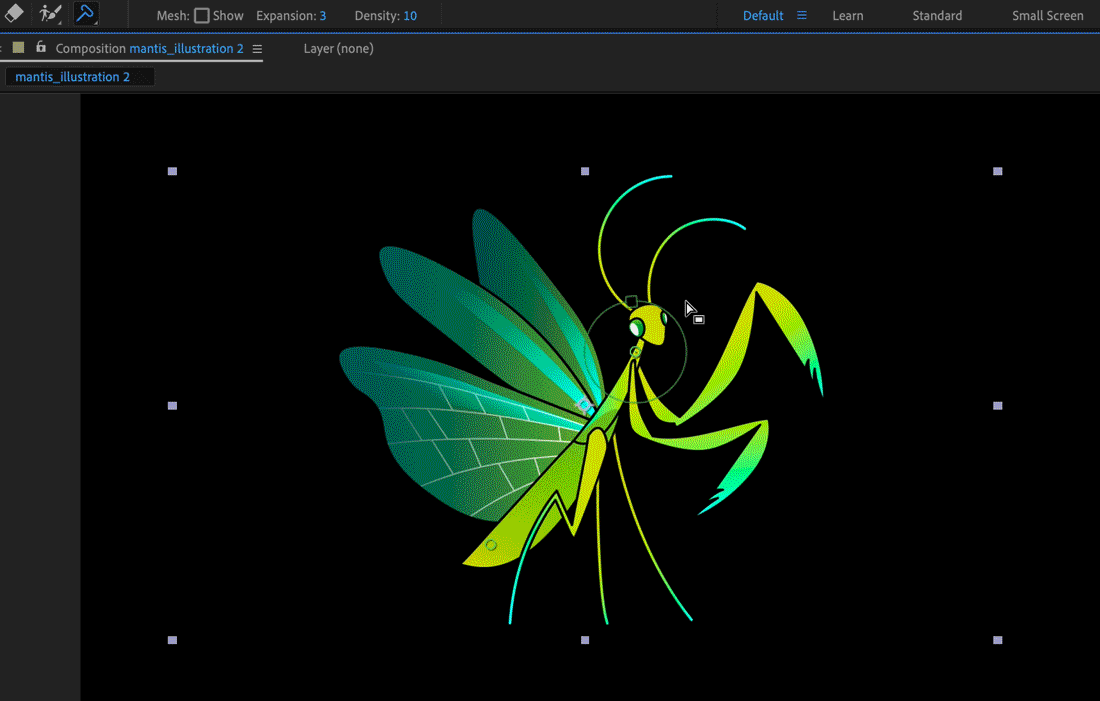
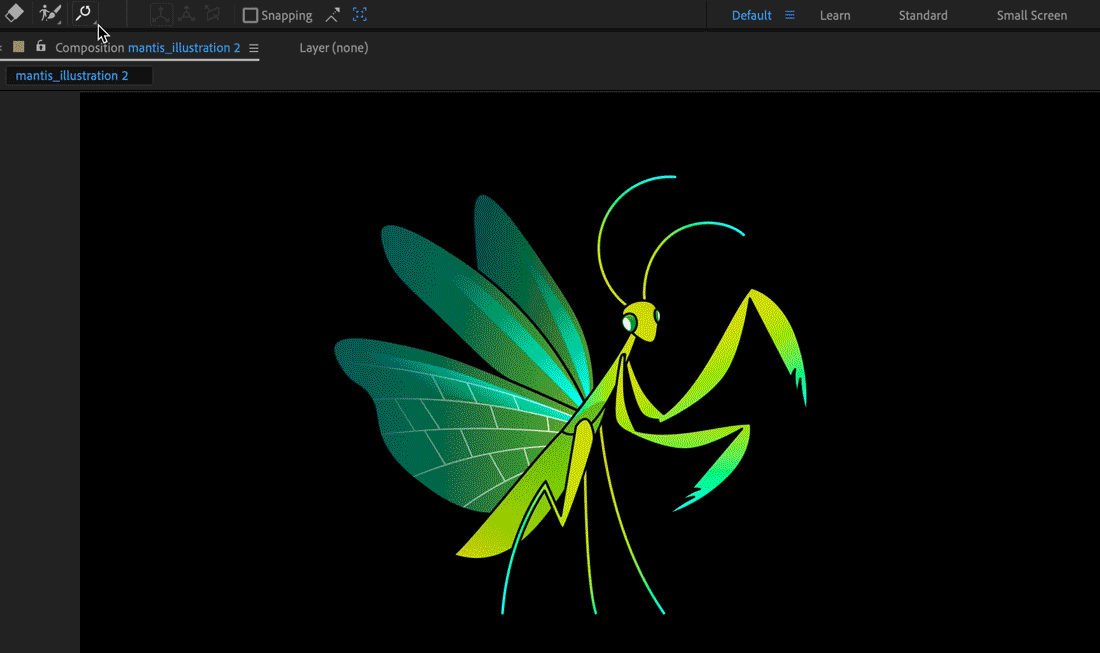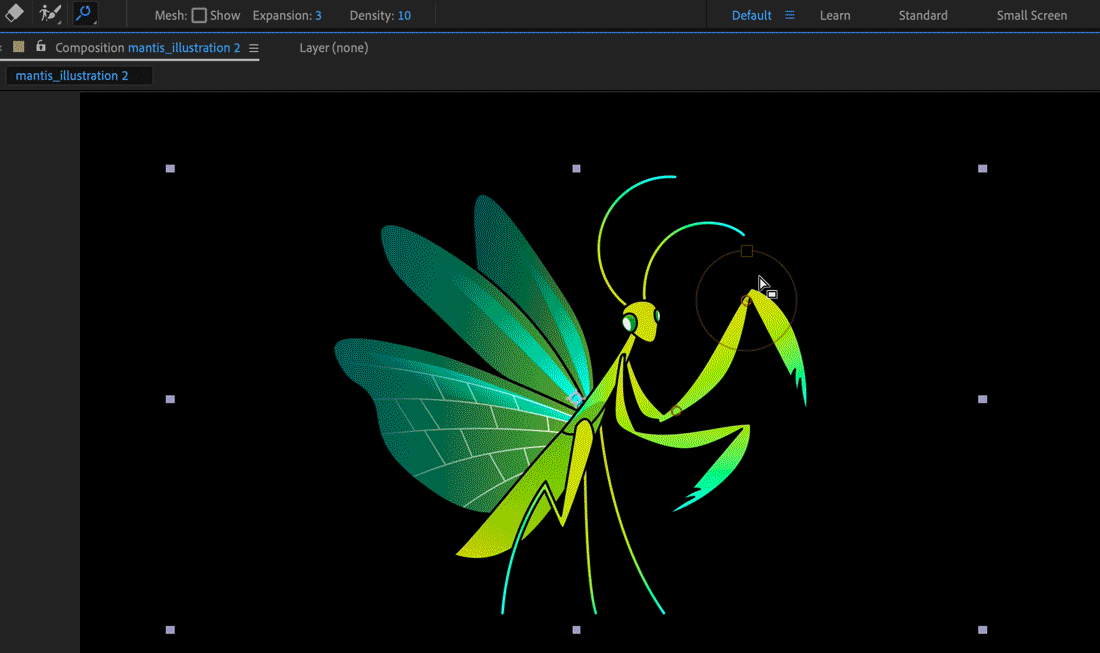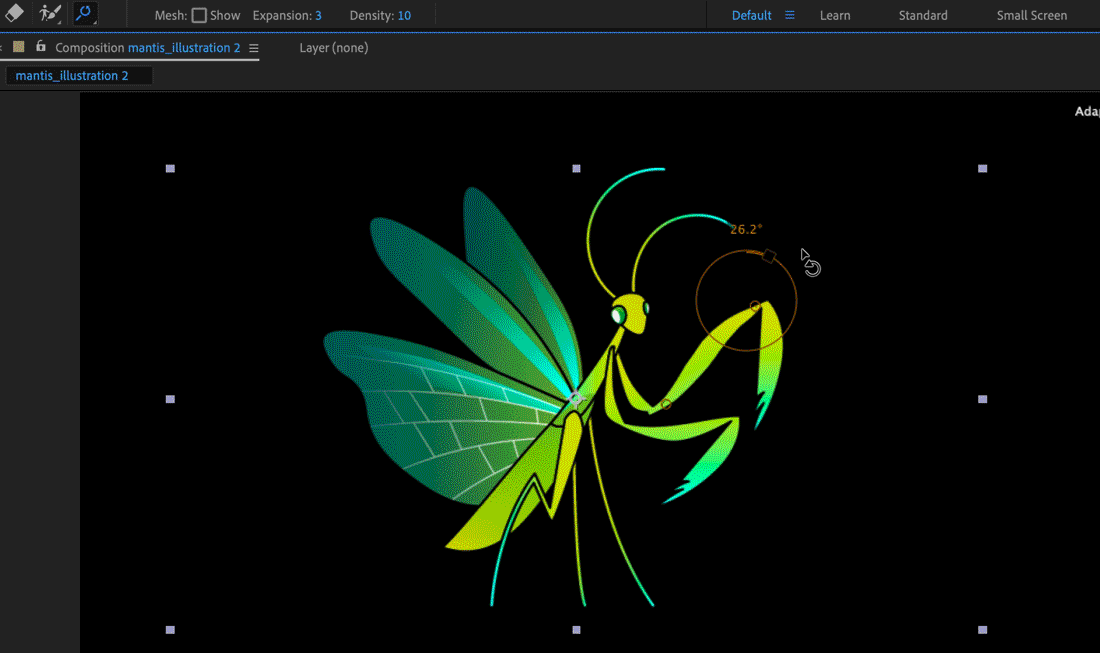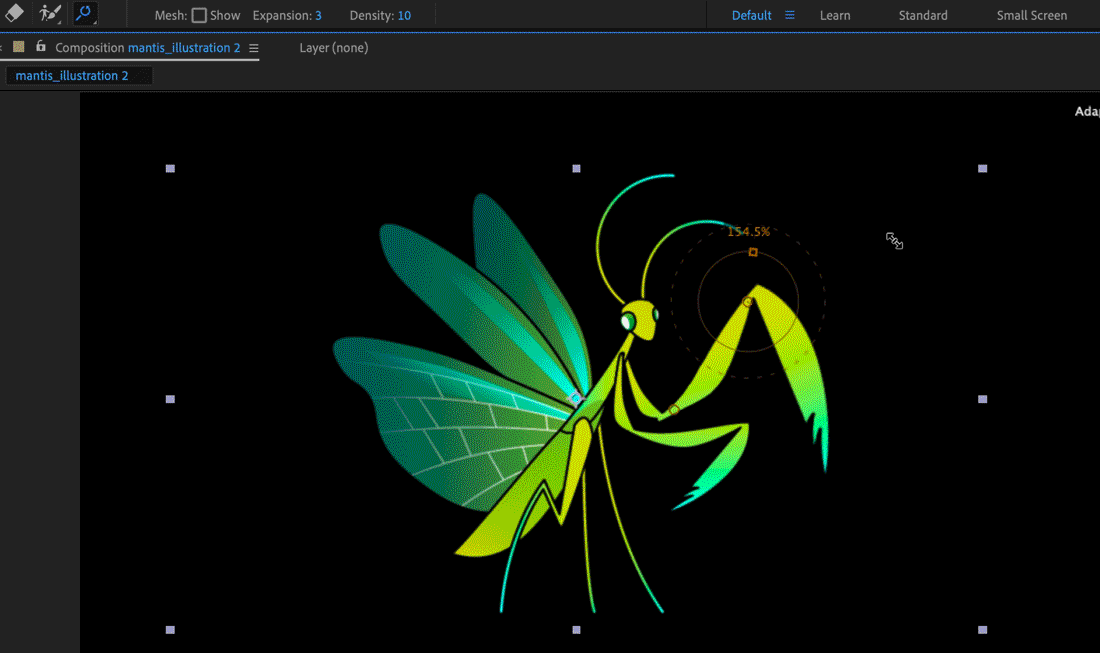
When you lot place the first pin, the area within an outline is automatically divided into a mesh of triangles. An outline is only visible when the Boob event has been applied and a Boob tool pointer is over the area that the outline defines. (See How the Puppet effect creates outlines.) Each part of the mesh is also associated with the pixels of the image, so the pixels move with the mesh.
To show the mesh, select Prove in the Tools panel.
When yous motility ane or more than Deform pins, the mesh changes shape to accommodate this motility, while keeping the overall mesh as rigid as possible. The result is that a movement in one office of the epitome causes natural, life-like movement in other parts of the image.
For example, if you identify Deform pins in a person's feet and hands and and then move one of the easily to brand information technology wave, the move in the attached arm is large, but the move in the waist is small-scale, but as in the real world.
If a unmarried animated Deform pivot is selected, its Position keyframes are visible in the Composition panel and Layer console as a motion path. You can work with these motion paths every bit y'all work with other move paths, including setting keyframes to rove across fourth dimension. (See Smooth move with roving keyframes.)
Yous can take multiple meshes on one layer. Having multiple meshes on one layer is useful for deforming several parts of an paradigm individually—such as text characters—as well as for deforming multiple instances of the same part of an image, each with a different deformation.
The original, undistorted mesh is calculated at the current frame at the fourth dimension at which you apply the effect. The mesh does non alter to conform motility in a layer based on motion footage, nor does the mesh update if y'all replace a layer's source footage detail.
Don't animate the position or scale of a continuously rasterized layer with layer transformations if you are too animating the layer with the Boob tools. The render society for continuously rasterized layers—such every bit shape layers and text layers—is unlike from the render order for raster layers. You tin can precompose the shape layer and apply the Puppet tools on the precomposition layer, or you can use the Puppet tools to transform the shapes within the layer. (Come across Render society and collapsing transformations and Continuously rasterize a layer containing vector graphics.)
The motion created by the Boob tools is sampled past motion blur if movement blur is enabled for the layer and the composition, though the number of samples used is half of the value specified by the Samples Per Frame value. (See Motion mistiness.)
You can use expressions to link the positions of Deform pins to motion tracking data, audio aamplitude keyframes, or whatever other backdrop.
Aharon Rabinowitz provides a tutorial on the Artistic COW website that shows a creative style to use the Puppet tools with a particle generator to simulate airflow over a car.
Robert Powers provides a video tutorial on the Glace Rock NYC website that demonstrates the use of parenting and the Puppet tools to breathing a character.
Dave Scotland provides a video tutorial on the CG Swot website that demonstrates how to create a looping character animation using the Puppet tools.
Daniel Gies provides a detailed serial of video tutorials in which he demonstrates the use of changed kinematics and the Boob tools to rig and animate a grapheme.
The stopwatch switch ![]() is automatically set for the Position property of a Deform pin every bit soon as the pin is created. Therefore, a keyframe is gear up or modified each time that you alter the position of a Deform pin. This motorcar-keyframing is unlike most properties in After Effects, for which yous must explicitly set the stopwatch switch by adding a keyframe or an expression to breathing each holding. The auto-animation of Deform pins makes it user-friendly to add them and animate them in the Composition panel or Layer console, without manipulating the backdrop in the Timeline panel.
is automatically set for the Position property of a Deform pin every bit soon as the pin is created. Therefore, a keyframe is gear up or modified each time that you alter the position of a Deform pin. This motorcar-keyframing is unlike most properties in After Effects, for which yous must explicitly set the stopwatch switch by adding a keyframe or an expression to breathing each holding. The auto-animation of Deform pins makes it user-friendly to add them and animate them in the Composition panel or Layer console, without manipulating the backdrop in the Timeline panel.
-
Select the layer that contains the image to animate.
-
Using the Puppet Pin tool
 , practice one of the following in the Limerick panel or the Layer panel:
, practice one of the following in the Limerick panel or the Layer panel: -
Click whatever nontransparent pixel of a raster layer to apply the Puppet issue and create a mesh for the outline created by motorcar-tracing the alpha channel of a layer.
-
Click within a closed path on a vector layer to apply the Puppet effect and create a mesh for the outline defined by that path.
-
Click inside a closed, unlocked mask to apply the Puppet upshot and create a mesh for the outline defined by the mask path.
-
Click outside all closed paths on a vector layer to utilize the Puppet consequence without creating a mesh. Outlines are created for paths on the layer, though an outline is only visible when a Puppet tool pointer is over the expanse that the outline defines. Place the pointer over the expanse enclosed by a path to run into the outline in which a mesh will exist created if you click that point. (Meet How the Boob upshot creates outlines.) Click within an outline to create a mesh.
A Deform pin is placed where yous clicked to create the mesh.
If an epitome is too complex for the Boob effect to generate a mesh with the current Triangle value, a "Mesh Generation Failed" message appears in the Info panel. Increment the Triangle value in the Tools panel and try again.
-
-
Click in one or more places within the outline to add together more than Deform pins.
Utilize as few pins as possible to attain your desired issue. The natural deformation provided by the Puppet result can be lost if y'all over-constrain the prototype. Just add together pins to the parts of the effigy that you know that you lot want to control. For example, when animative a person waving, add a pin to each human foot to hold them to the footing, and add together a pin to the waving hand.
-
Go to another time in the composition, and move the position of 1 or more of the Deform pins past dragging them in the Composition or Layer panel with the Puppet Pin tool. Repeat this step until yous have completed your blitheness.
Yous can alter the motion paths of the Deform pins using the same techniques that you lot employ to modify whatsoever other motion paths.
Later Effects no longer draws the tinted fill for the original layer region when hovering using the Puppet Pin tool.
Y'all can sketch the motion path of i or more Deform pins in real time—or at a speed that y'all specify—much as yous tin can sketch the motion path of a layer using Motion Sketch.
If your limerick contains audio, you lot can sketch movement in time with the audio.
Before you begin recording movement, yous may want to configure settings for recording. To open the Puppet Record Options dialog box, click Record Options in the Tools panel.
Speed
The ratio of the speed of the recorded movement to speed of playback. If Speed is 100%, the motion is played back at the speed at which it was recorded. If Speed is greater than 100%, the motility plays back slower than it was recorded.
Smoothing
Prepare this value college to remove more than extraneous keyframes from the motion path equally it's drawn. Creating fewer keyframes makes motion smoother.
Use Draft Deformation
The distorted outline that is shown during recording does not take Starch pins into account. This option can improve performance for a complex mesh.
-
Select one or more Deform pins.
-
Go to the time at which to begin recording motion.
-
In the Composition panel or Layer console, hold the Ctrl (Windows) or Command (Mac OS) cardinal to activate the Puppet Sketch tool. Ctrl-elevate (Windows) or Control-drag (Mac Os) the pins to breathing.
Recording of motion begins when you click to brainstorm the drag. Recording ends when you lot release the mouse button.
The color of the outline for the mesh for which motion is being sketched is the same as the color of the pin (yellowish). Reference outlines, for other meshes on the same layer, match the characterization color of the layer.
The electric current-time indicator returns to the fourth dimension at which recording began, so that you lot can repeat the recording operation with more Deform pins or redo the recording operation with the aforementioned pins.
You can alter the move paths of the Deform pins using the same techniques that y'all utilize to change any other motion paths. The motion path for a pin is shown but if it is the merely pin selected.
Endeavour creating several duplicate meshes and sketching motion for each mesh. When you accept multiple meshes in the same example of the Puppet event, you tin can sketch motion for one mesh while seeing the reference outlines of the others, assuasive you to follow their movements, either roughly or precisely.
How the Puppet event creates outlines
When a Boob mesh is created, its boundaries are adamant by an outline, which can be divers by whatever of the following types of airtight paths:
-
An unlocked mask path
-
A shape path on a shape layer
-
A text character's outline
If a layer has no unlocked masks, shapes, or text characters on it when you utilize the Puppet result, information technology uses Auto-trace to create paths from the alpha channel. These paths are only used past the Boob outcome in the determination of outlines and do not announced equally masks on the layer. If the layer is a raster layer with no alpha channel, the result is a single rectangular path around the bounds of the layer. For a complex image, or to configure Auto-trace settings, use Auto-trace before using the Boob tools. (See Create a mask from channel values with Machine-trace.)
A text character that consists of multiple disjoint closed paths (such equally the letter i) is treated equally multiple dissever paths.
The stroke of a shape or text graphic symbol is not used in the decision of outlines; only the path is used. To encompass a stroke within a mesh created from such items, increase the Expansion value. The default value of 3 pixels for Expansion encompasses a stroke that extends iii pixels or less from its path.
Apply pigment strokes to a layer using the Brush tool with the Pigment On Transparent pick. Painting with this choice selected creates a raster layer with only the pigment strokes, defined by an blastoff aqueduct. Yous can and so utilise the Puppet tools to breathing the paint strokes. Do not utilise a mask on the layer.
If multiple masks, shapes, or characters overlap on the same layer, an outline is created from the union of the overlapping shapes, overlapping characters, or overlapping masks. If a mask overlaps a text graphic symbol or shape, outlines are created for the unabridged character or shape, for the portion of the character or shape that is inside the mask, and for the mask itself.
To distort multiple disjoint characters or shapes as one object, surround the individual objects with a mask (with mask mode set to None), and utilize the mask path as the outline with which to create the mesh. Yous can delete the mask afterward you lot have created the mesh.
If the Puppet upshot has already been applied to a layer, outlines appear with a yellowish highlight equally you motion a Puppet tool pointer over them. Y'all can cull the outline in which to place an initial pin to create a mesh. A mesh is created each fourth dimension that you click within an outline with a Boob tool.
If the Puppet effect has not already been practical to a layer, outlines for that layer have not yet been calculated. When you click, the Puppet effect calculates outlines and determines whether yous accept clicked within an outline. If then, information technology creates a mesh defined by the outline in which you clicked. Otherwise, you can move the pointer around in the layer to select the outline in which to place a pivot and create a mesh. Moving the pointer around in the layer is useful for seeing the outlines of various objects and choosing which outlines to use to create a mesh.

Work with Puppet pins and the distortion mesh
- To evidence the mesh for the Puppet effect, select Bear witness in the options section of the Tools console.
- To select or movement a pin, click or drag it with the Move tool
 . To activate the Move tool, place the pointer on a pin while either the Selection tool
. To activate the Move tool, place the pointer on a pin while either the Selection tool  or the corresponding Puppet tool is active.
or the corresponding Puppet tool is active. - To select multiple pins, Shift-click them, or use the marquee-option tool
 to drag a marquee-option box effectually them. To activate the marquee-option tool, place the pointer for a Puppet tool outside all meshes and outlines or concur the Alt (Windows) or Choice (Mac Os) key.
to drag a marquee-option box effectually them. To activate the marquee-option tool, place the pointer for a Puppet tool outside all meshes and outlines or concur the Alt (Windows) or Choice (Mac Os) key. - To select all pins of one kind (Deform, Starch, or Overlap), select one pin of that kind and press Ctrl+A (Windows) or Command+A (Mac OS).
- To delete selected pins, press the Delete primal. If the pin has multiple keyframes, and but the keyframe at the current fourth dimension is selected, pressing Delete deletes only that keyframe; pressing Delete once again deletes the pivot.
- To reset Deform pins to their original locations at the current time, click Reset for the Puppet effect in the Timeline panel or Effect Controls panel. To remove all pins and meshes from an instance of the Puppet issue, click Reset over again.
Sometimes, yous want to breathing an prototype from an initial position, through an intermediate position, and dorsum to the initial position. Rather than manually dragging the pins back to their initial positions at the end of the animation, identify the current-time indicator at the end time and click Reset. Only the keyframes at the current time are reset.
- To increase or decrease the number of triangles used in a mesh, modify the Triangle value in the options section of the Tools panel or in the Timeline panel. Modifying the Triangle value sets the value for a selected mesh or, if no mesh is selected, sets the value for meshes created later.
A college number of triangles gives smoother results but takes longer to return. Small objects, like text characters, usually distort well with only fifty triangles, whereas a large effigy may require 500. The number of triangles used may not match the Triangle value exactly; this value is a target only.
- To aggrandize the mesh across the original outline, increment the Expansion belongings in the options department of the Tools console or in the Timeline panel. Modifying the Expansion property sets the value for a selected mesh or, if no mesh is selected, sets the value for meshes created later. Expanding the mesh is useful for encompassing a stroke.
- To indistinguishable an object using Puppet Pivot tool, click inside the original outline. Clicking within the original outline creates a new mesh, with its ain copy of the pixels from within the original outline. You tin also duplicate a Mesh group in the Timeline panel to achieve the aforementioned result, which is sometimes easier than clicking within the original outline without clicking the mesh to create a pivot.
Puppet Overlap controls
When y'all are distorting 1 part of an image, y'all may want to command which parts of the image announced in front of other parts. For example, you may desire to keep an arm in front end of the confront as you make the arm wave. Utilize the Boob Overlap tool to apply Overlap pins to the parts of an object for which you want to control apparent depth.
Yous apply Puppet Overlap pins to the original outline, not to the deformed image.

Each Overlap pin has the post-obit properties:
In Front
The apparent proximity to the viewer. The influence of Overlap pins is cumulative, meaning that the In Front values are added together for places on the mesh where extents overlap. Y'all can employ negative In Front values to abolish out the influence of another Overlap pivot at a specific location.
An surface area of the mesh that is not influenced past Overlap pins has an implicit In Forepart value of 0. The default value for a new Overlap pin is 50.
When animating the In Forepart value, you should unremarkably use Hold keyframes. You do not usually want to interpolate gradually from an element being in front end to an element beingness in back.
Extent
How far from the Overlap pin its influence extends. The influence ends abruptly; it does not decrease gradually with distance from the pin. Extent is indicated visually by a fill up in the affected parts of the mesh. The fill is dark if In Front is negative; the fill is low-cal if In Front end is positive.
Puppet Starch controls
When yous are distorting one part of an prototype, you may want to forestall other parts from being distorted. For example, y'all may want to preserve the rigidity of an arm as you motion a manus to brand it wave. Use the Puppet Starch tool to use Starch pins to the part of an object that you desire to proceed rigid.
You apply Puppet Starch pins to the original outline, not to the plain-featured image.

Each Starch pivot has the post-obit properties:
Amount
The strength of the stiffening agent. The influence of Starch pins is cumulative, meaning that the Amount values are added together for places on the mesh where extents overlap. You lot can use negative Corporeality values to cancel out the influence of another Starch pin at a specific location.
If yous notice image tearing near a Deform pivot, use a Starch pivot with a very small Amount value (less than 0.i) near the Deform pin. Small Amount values are practiced for maintaining paradigm integrity without introducing much rigidity.
Extent
How far from the Starch pin its influence extends. The influence ends abruptly; it does not decrease gradually with distance from the pin. Extent is indicated visually by a pale make full in the affected parts of the mesh.
In improver to animating all the same images, you tin utilize the Puppet effect on a layer with motion footage as its source. For instance, you could distort the contents of the entire composition frame to match the movement of an object within the frame. In this case, consider creating a mesh for the entire layer, using the layer boundaries as the outline, and using the Boob Starch tool around the edges to preclude the edges of the layer from distorting.
The Puppet tools and Puppet issue in After Effects utilize an enhanced puppet engine called the Advanced Puppet Tool, and the onetime engine is called the Legacy puppet engine. In After Effects xv.1 and later, the Advanced puppet engine is the default engine for your projects. Projects saved in before versions of After Effects employ the legacy Puppet engine by default. To access the Advanced Puppet Tools, click the Pin icon in the Toolbar and the Puppet group is displayed in the Timeline panel.
At the cadre, the avant-garde boob engine apply similar concept equally the legacy puppet engine, the differences being:
- New pin behaviors and pin types
- Smoother and customizable deformations
- Enhanced density
Difference between Legacy puppet engine and Advanced puppet engine

Refer to the table below to understand the key differences betwixt the Legacy and Avant-garde boob engines:
| Legacy puppet engine | Avant-garde boob engine |
|---|---|
| Triangle command: Specifies the highest number of triangles allowed for a mesh. Legacy Puppet Tool uses smart triangle placement in the mesh with a college density of triangles to achieve meliorate results. | Density command replaces the Triangle control. Density controls the layout, size, and amount of triangles automatically calculated within a mesh. With higher density, the maximum and minimum triangle sizes reduce, you can add together more triangles betwixt pins, and the maximum number of triangles allowed take increased. Lower the density, the triangle size increases and creates a sparse mesh. |
| Starch pins are under the Stiffness group. | Starch pivot are under the Deform group and the Stiffness group is discontinued. |
| Starch pins accept Extent command to manipulate the extent to which the pin impacts the boob. | Starch pins exercise not accept Extent control, but tin bear on the stiffness in the region between Starch pins and other pins. The Advanced puppet engine interprets the Starch pins every bit Position pins. |
| You can't convert Starch pins into whatever other form of pins. | You can convert Starch pins into Position pins with the Pin Type holding. |
| No selection of Mesh Rotation Refinement. | Mesh Rotation Refinement, specifies the maximum amount whatever position or starch pin rotates to minimize deformation. Higher the value, higher is the corporeality of rotation (flexible deformation), and lower the value, lower is the amount of rotation (stiff deformation). |
You can apply the Puppet Engine control to cull between the Advanced boob engine and the Legacy puppet engine. To choose, in the Timeline panel, click the drop-down menu adjacent to Puppet engine, and select the engine. You tin can switch between the 2 engines but Afterwards Effects recommends that y'all avoid switching afterwards y'all place or breathing pins for the following reasons:
- As the two engines interpret pins differently, switching could change the deformation.
- Starch pins are different in Advanced boob engine and so the Legacy puppet engine treats advanced starch pins, as normal position pins, and the Advanced puppet engine ignores legacy starch pins.
The Advanced Boob Tool offers the following types of pins to animate your puppets. To apply these pins, select the pin type in the Boob Tool carte in the toolbar.
- Boob Position Pivot Tool: The pins yous place with this tool tin but control the position of the pin. These pins display as yellow circles in the UI.
- Puppet Starch Pin Tool: These pins display as carmine circles in the UI.
- Puppet Overlap Pin Tool: These pins display as blueish circles in the UI.
- Advanced Pins: Enables you to control the position, scale, and rotation of the pin. This allows significant control over how the Puppet effect mesh deforms around that pin. The mesh tin create noticeable shearing if you do not animate all three backdrop. For example, you can utilise an advanced pin to breathing the head of a character to motion to the side and look downwards. However, if y'all practise not animate the rotation manually, the head continues to signal in the same management and create a stretched appearance. These pins display as bluish-green circles in the UI.
- Bend Pins: These pins automatically summate their location from the surrounding pins, similar to starch pins, while assuasive you to command of the scale and rotation of the pin. Yous tin use the bend pins to create the advent of the chest of the character breathing, or of a wagging tail. Some other instance can exist where y'all scale or rotate a office of the mesh but have the position of the pin automatically movement with the balance of the puppet. These pins display as orange-dark-brown circles in the UI.
Work with advanced pins and bend pins
The avant-garde pins and bend pins have controls to adjust calibration and rotation:
When yous select curve pins or advanced pins in theBoob Tool panel, it displays a rotation and scale control - larger, outer circle with a single square handle.
Employ the post-obit steps to change the rotation and scale controls:
-
To change rotation, click anywhere on the outer circle and drag around the circle.
-
Concur the Shift key while you lot drag to constrain rotation to xv caste increments.
-
To modify calibration, click the foursquare handle and drag in or out from the outer circle.
-
Agree the Shift key while you drag to constrain scale to v% increments.
- You tin switch the existing pin types between Position and Starch.
- The Puppet Starch tool has a different icon, and is second in the listing of Puppet tools in the Toolbar console.
- Path Bespeak and Handle Size options in Preferences > Full general touch pin size. Also when you hover the mouse over the pins, they increment in size.
- The Puppet effect ignores masks ready to None, or any mask used by an effect as a mask reference (event properties > Compositing Options > Mask Reference), when computing the mesh outline.
Source: https://helpx.adobe.com/after-effects/using/animating-puppet-tools.html
Posted by: roddeneaddelartion.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Use Animator In Marquee Avid"
Post a Comment