What Is Different About A Plant And Animal Cell
The difference between plant and brute cytokinesis is mainly due to the following factors like:
- Mode of cytokinesis
- Cell abscission
Both the constitute and the animal cell divides their cytoplasmic contents as betwixt the ii identical daughter cells but through different mechanisms. In a found cell, the cytoplasmic division occurs via the fusion of phragmoplast associated vesicles at the metaphase plate. Oppositely, animal cell cytokinesis occurs via constriction of the concentric contractile ring towards the heart of the cell.
Cell abscission is a stage, during which a mother jail cell separates into two halves with the aforementioned nucleocytoplasmic material. Cell abscission In a plant prison cell takes identify through the expansion of cell plate towards the periphery. In contrast, cell abscission in the fauna cell occurs via the ingression of cleavage furrow towards the heart.
Content: Establish Vs Beast Cytokinesis
- Comparison Chart
- Definition of Cytokinesis
- What is Cytokinesis in Plants?
- What is Cytokinesis in Animals?
- Fundamental Differences
- Similarities
- Conclusion
Comparison Nautical chart
| Backdrop | Institute Cytokinesis | Animal Cytokinesis |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Institute jail cell cytokinesis is a kind of cell motion or prison cell sectionalisation, which forms 2 identical cells afterward a cell divides through the jail cell plate expansion | Animal cell cytokinesis is a kind of cell motion or prison cell division, which forms ii identical cells subsequently a jail cell divides through the prison cell constriction or furrowing |
| Mode of cytokinesis | Here, the cytokinesis occurs via a cleavage furrow or jail cell constriction machinery | Here, the cytokinesis occurs via the fusion of phragmoplast associated associated vesicles |
| Occurrence | Information technology begins from the prophase cell stage | It begins from the anaphase cell phase |
| Cell partition | A establish cell partitions its cellular material equally between the two identical cells through the germination of concentric contractile microfilament ring | Animal jail cell partitions its cellular cloth equally between the two identical cells through the formation of cardinal cell plate |
| Spindle fibres | Remnants of the spindle fibres persist | Hither, the spindle fibres degenerate |
| Cleavage furrow | Here, the formation of cleavage furrow doesn't appear | The formation of cleavage furrow occurs in the beast cell as a consequence of in constriction of the actin band |
| Vesicle formation | Small membrane-bound vesicles are derived through the Golgi trunk | There is no such vesicle formation |
| Vesicle fusion | Here, the vesicles fuse that outcome in the prison cell plate formation past depositing the starchy textile | Here, no such fusion occurs |
| Mid-torso | Prison cell plate acts every bit a mid-body that contains remains of mitotic spindles and vesicles filled with cellular fabric | The contractile band acts as a mid-body that possesses actin and myosin filaments |
| Mid-trunk expansion | The mid-trunk extends from the eye to the lateral ends | The mid-body ingresses towards the centre from the peripheral ends |
| Cell abscission | Female parent cell separates via centrifugal expansion of the cell plate | Mother cell separates via centripetal expansion of a cleavage furrow |
Definition of Cytokinesis
The term cytokinesis merely refers to the jail cell motion or jail cell division. It is defined equally a course of cytoplasmic sectionalization, which occurs after the chromosomal separation. In plants, the cytokinesis usually begins from the prophase stage of the cell cycle and lasts to the telophase stage. Oppositely, cytokinesis in the fauna cells begins from the anaphase stage and occurs concurrently till the telophase stage of the cell bicycle. It is the final phase of the jail cell bicycle (both mitosis and meiosis), which divides a cell into two. Generally, the process of cytokinesis involves:
- The formation of the midbody
- Expansion or contraction of the midbody
- Cell division
- Formation of two identical daughter cells
Thus, it is a cell sectionalisation that facilitates the equal distribution of the cellular contents between the ii daughter cells in instance of both plant and animate being cells. It is an important result, which decides the successfulness of all the previously occurred mitotic events. Cytokinesis is the concluding, but the most crucial stage of the cell division cycle that is necessary for the growth and development of all the living cells, including plants and animals. But, the mechanism of cytokinesis in both the found and animal cells differ, which we fill farther study in this article.
What is Cytokinesis in Plants?
Cytokinesis in plants is divers as one of the cytological events, which uniformly divides the cellular contents of the mother cell between the 2 daughter cells, every bit the jail cell partitioning occurs via the fusion of phragmoplast associated vesicles.
Here, the microtubule-organizing centres course microtubules, and the Golgi body synthesizes many small membrane-bound vesicles that are filled with the cytoplasmic material of the plant cell.
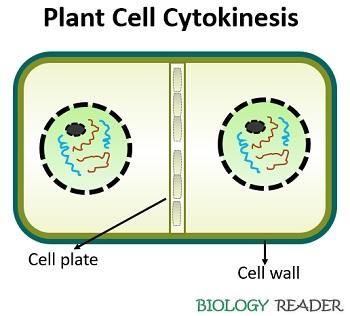
During the telophase stage, the microtubules remnants or phragmoplast forms at the centre of the prison cell. The vesicles walk through the microtubules to reach the equator of the phragmoplast. Eventually, the vesicles will fuse.
The fusion of vesicles results in deposition of the starchy material within the plant cell, which is called a cell plate formation. And so, to form the jail cell wall, a few polysaccharide vesicles fuse to extend the jail cell plate laterally. As a result, the cell plate ultimately merges with the cell membrane and separates the parent prison cell into ii identical daughter cells.
What is Cytokinesis in Animals?
Cytokinesis in animals is defined as one of the cytological events that evenly distributes the cell material of the parent cell between the two daughter cells later the cell partition occurs through a cleavage furrow or cell constriction method. It starts from the anaphase stage and occurs meantime till the telophase stage of the cell cycle. The microfilaments tuck to form a concentric contractile ring in betwixt the animal cell.
The concentric contractile ring acts as a mid-body that contains contractile bundles of the actin and myosin-Two filaments. Actin filaments form at the sectionalization plane, and the myosin filaments pull these to form a ring-similar structure inside the cell. This contractile band gradually contracts towards the centre or moves to the inwards direction, by making a cleavage furrow.
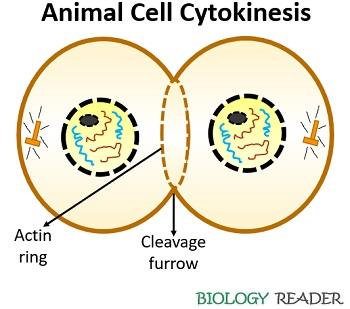
A cell facilitates the uniform distribution of the cytoplasmic and nuclear contents through the mid-body. Then, cell abscission occurs as the cleavage furrow ingresses from the periphery towards the centre, which results in cell partitioning of the parent cell. 2 nascent cells will be produced later the prison cell sectionalisation, where each will have the same proportion of the cytoplasmic material.
Key Differences Between Plant and Fauna Cytokinesis
- Cytokinesis merely refers to the process of cell motion or cell partitioning, in which both a plant and animate being jail cell develops into two nascent cells via a cell plate and contractile ring formation, respectively.
- The mode of cytokinesis is one of the most critical features that differentiate the mechanism of the cell division in the plant and animal cell. A found cell produces daughter cells by the cell-constriction mechanism or through the germination of cell-furrow. Oppositely, the animate being cell forms two nascent cells by the fusion of phragmoplast associated vesicles at the metaphase plate.
- Vesicles form during the telophase stage of the constitute cell, which afterwards moves towards the phragmoplast and fuse with each other to develop a thick prison cell plate. But, there is no such vesicle formation, and fusion occurs during the cytokinesis of the animal cells.
- Jail cell abscission occurs via a centripetal expansion of the contractile band in animals, and through centrifugal expansion in plant cells.
- The formation of a mid-body during the cytokinesis process is one of the near hitting features that differentiate the institute and fauna jail cell cytokinesis. A found cell possesses a mid-body of phragmoplast (remains of mitotic spindles) and some vesicles filled with the cellular material. In contrast, an animal cell has a mid-torso of actin and myosin-II microfilaments that form a concentric contractile band within the cell.
Similarities
- Both the establish cell and animal cell cytokinesis are essential for cell growth and development.
- The jail cell sectionalization in plant and animate being cell facilitates the equal distribution of the nuclear and cytoplasmic contents between the two daughter cells.
- Both the plant jail cell and animal cell cytokinesis lasts till the telophase stage of the cell division wheel.
- Both the processes occur after the chromosomal segregation.
Decision
Thus, we can conclude that the procedure of cytokinesis is a crucial event in the cell cycle that ensures the uniform partitioning of the nuclear and cytoplasmic contents betwixt the 2 developing cells. Cytokinesis generally involves the extensive restructuring of the cellular contents, and information technology begins later on the chromosomal segregation. In both found and brute cell, the result of cytokinesis is a pivotal step for cell growth and development.
Source: https://biologyreader.com/difference-between-plant-and-animal-cytokinesis.html
Posted by: roddeneaddelartion.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is Different About A Plant And Animal Cell"
Post a Comment